Both incremental encoders and absolute encoders are some of the best tools to use for manufacturing, servo, and DC motors. However, there are vast differences between the two that will determine which one is more appropriate for your project. By far, incremental encoders will be a better choice for more simple quality checks and counts, while absolute rotary encoders are better for systems that require a precise location for safety reasons and quality checks.

Incremental Vs Absolute Encoder: Their Differences & How to Choose?
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Incremental Encoder?
An incremental encoder is a type of encoder that uses a circular disc, rotating shaft, and fixed light or magnet to produce an output signal through digital or pulse signals. Incremental encoders usually produce square waves and simple signals to measure the incremental change and position of an object.
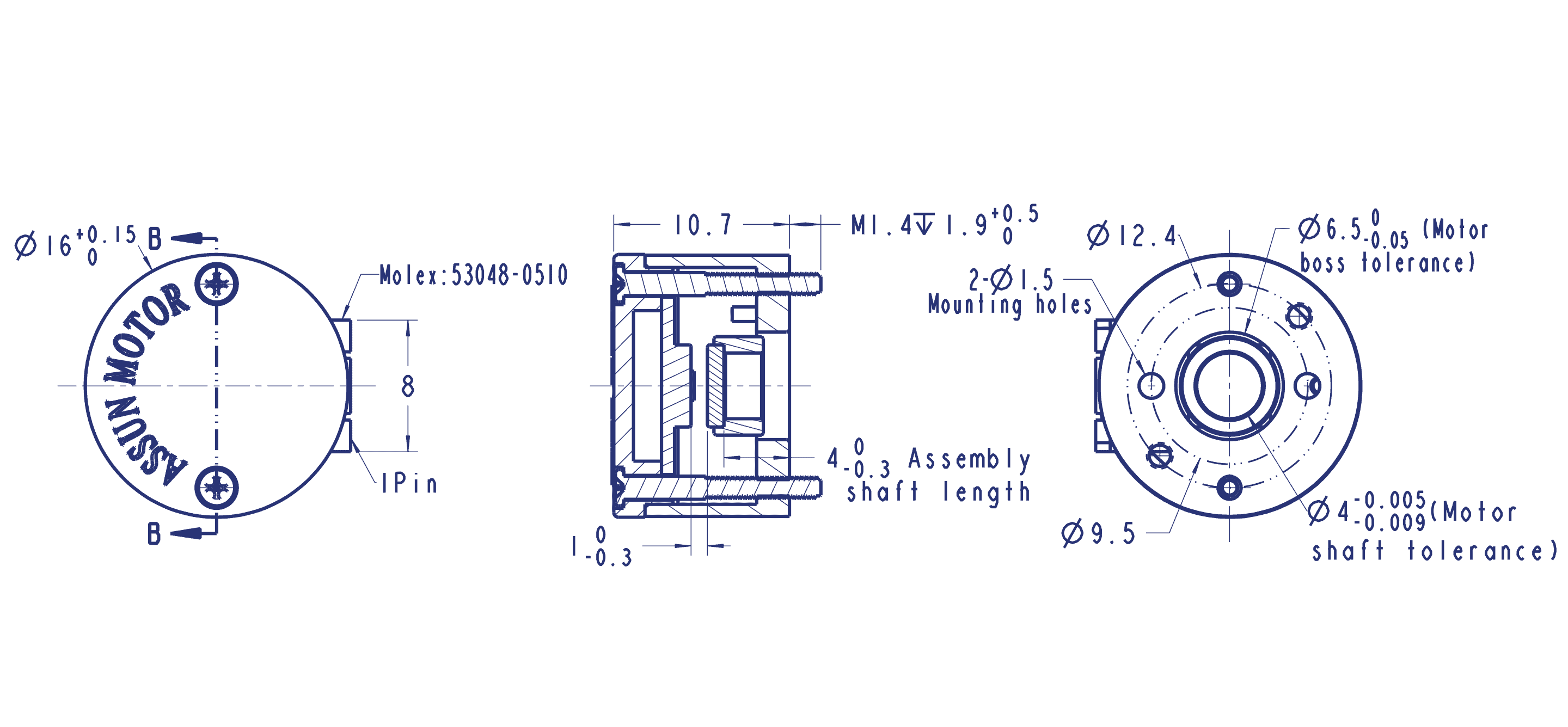
Assunmotor’s Incremental Encoder (Electromagnetic Type) – Cross Section
Working Principle of Incremental Encoder
An incremental encoder is much less sophisticated than an absolute encoder but is still essential in certain industries. It produces a measurement of position and distance by using the relative position of an object and a starting point.
The most popular types of incremental encoders are rotary encoders. Rotary encoders work by positioning a circular, rotating disc in between a fixed light and a transducer, or a fixed magnet. As the disc spins, there are slots that are positioned uniformly throughout it, almost resembling the spokes of a wheel.
Incremental encoders will have more uniform slots located throughout the disc, whereas an absolute encoder will have more intricate slots decorating the outside the disc. These incremental slots will occasionally let in a light signal or a magnetic signal, depending on whether a machine is using an optical encoder or electromagnetic encoder. Assun Motors carries both electromagnetic and optical encoders, with our optical encoders being the more popular choice.
As the disc rotates on a shaft, light passes through the opening and blocked by the opaque areas of the disc. When light passes through an opening, it hits the transducer on the other side of the disc, producing an output signal that can then be interpreted digitally.
This output signal is determined by measuring the signals per revolution. The incremental encoder’s simple measurement can help provide information on distance, speed, and position relative to another object.
Most incremental encoders will produce square waves, although some of them can produce sine or cosine waves. A magnetic encoder works in much the same way. However, a magnetic signal will trigger the sensor and produce a square wave when a charge changes, or when a charge remains the same.
How Incremental Encoder Behaves?
Incremental encoders are incredibly reliable tools, which is why they are used in a variety of industries such as assembly machines, PCB boards, and canning.
The incremental encoder will, from time to time, face errors, especially if there is a power outage. Once it produces an output signal, the manufacturer will know the relative position of an object, its distance, and other basic information.
However, as the name suggests, an incremental encoder cannot produce information on where the absolute position of an object is. The absolute position of an object is the position of the object in real-time. Only an absolute encoder will be able to produce this information.
Incremental encoders work well in environments that require simple counts or updates. For instance, incremental encoders work well in assembly lines, where the only requirement is to understand where an object is in reference to another object. Incremental encoders can also be found in robotics assembly lines, since these are also simple processes that benefit from their small size.
Another popular use of incremental encoders is in counts. For instance, let’s say you measure an object at 5000 counts. The incremental encoder will again capture the object again when it was reached 7,000 counts. Using simple math lets the assembly line personnel know that the object has moved 2,000 counts, therefore providing information on how fast the assembly line is moving and what its current load is.
Pros & Cons of Incremental Encoder
One of the best pros of an incremental encoder is its ability to be used in virtually any type of assembly line. They are quite affordable, more so than incremental encoders.
In addition, they are also available as multi-turn encoders. When used as a multi-turn encoder, they can produce information about the degree of rotation and a total number of rotations of an object. This is a great addition to industries that require measuring longer lengths of linear applications, such as particularly long conveyor belts.
However, the biggest con about incremental encoders is their inability to reveal information about the exact position of an object, also known as its absolute position. In addition, incremental encoders can only produce pulse signals if there is another point of reference for the object. In case of a power failure, you will need to restart your incremental encoder over again, which can be inconvenient and slow down production times.
Pros ![]()
- More affordable than an absolute encoder.
- More versatile.
- Can be used for long and short applications.
- Can determine relative position and counts.
Cons ![]()
- Will not work in immediately after a power outage.
- Requires starting reference point.
What is an Absolute Encoder?
An absolute encoder is somewhat similar to an incremental encoder. However, its main feature is that it is able to produce a pulse signal that measures the absolute position of an object, no matter where it currently is in space or in a factory line. This is known as measuring the angular position of an object.
Absolute encoders are available in a variety of models, just like incremental encoders. However, the most popular types of models will be an optical absolute encoder and an electromagnetic absolute encoder.
Assunmotors also offers absolute rotary encoders for applications that require high-quality assurance and safety. For instance, if you have an assembly line that needs to know where a certain object is at all times for safety reasons, it’s best to purchase an absolute encoder. Absolute encoders can also come in a variety of styles, including linear and rotary styles.

Cross Section of Assunmotor Absolute (Electromagnetic type) Encoder
Working Principle of Absolute Encoder
At first glance, an absolute encoder might appear to be the same as an incremental encoder. On the contrary, its job is to measure position every time an object moves, creating the most up-to-date information about the position of an object.
The disc of an absolute encoder is much more intricate. Instead of having uniformly spaced slots on its disc, like an incremental encoder, this encoder is used to measure changing positions. Thus, there are unique patterns placed on the encoder that is custom-designed to fit the production or assembly line.
For example, if you look at the disc of an incremental encoder, you will notice it has distinct spokes on either side of the disc, almost resembling the shape of a pie or perfectly cut triangles in a circle. On the other hand, looking at an absolute encoder produces the opposite effect. There are intricately detailed designs that provide a unique code when the absolute encoder is put to work in a machine.
Once light enters through these slots, it again hits a transducer which can interpret the signal digitally. However, the pulse signals offer a unique code that is interpreted much differently. These signals are not square pulse waves, like those from an incremental encoder. They are much more complex and need to be interpreted by a trained manufacturer.
Pros & Cons of Absolute Encoder
Perhaps the biggest benefit of an absolute rotary encoder is its ability to determine absolute position every time the machine is turned on. On the contrary, an incremental encoder will need to be reset during every use, since it needs to work with the relative position of another object.
Another main pro when it comes to absolute and incremental encoders, is that absolute encoders will work even when there is a power shutoff. If the building or factory were to lose power, an absolute encoder will start up again counting as usual.
Absolute encoders also produce a unique binary code along with a specific angle for an object. When combined, the unique binary code and angular position of an object allows manufacturers to know where in line an object is, how far it has traveled, and keep track of it even after a power outage.
Absolute encoders might be a bit more pricey when it comes to design. However, they are well worth the cost for industries that require a safer alternative, and industries that can’t afford to lose out on a single day or production.
For instance, you might see absolute rotary encoders used in fields such as surgical robotics, where the robot must be absolutely careful that it is not operating over the same area. This is one of the best examples of how absolute encoders can be used for accuracy and safety.
You might also see absolute encoders used in areas such as printing. When an absolute encoder measures that printing has stopped, it can then turn out a newspaper and begin the process over again. If power outage again, this will not impact deadlines or the flow of the absolute encoder.
Pros ![]()
- Tells Absolute Position.
- Works Even During Power Outages.
- Better for Safety.
- Provides Unique Codes.
Cons ![]()
- More Expensive than incremental encoders.
- A bit difficult to manufacture.
Comparing Incremental and Absolute Encoders (Table)
Absolute Encoder | Incremental Encoder |
|
|---|---|---|
| Produce Code on Absolute Position | Yes | No |
| Cost less for manufacturers | No | Yes |
| Can be used where safety is paramount | Yes | No |
| Come in optical and electromagnetic models | Yes | Yes |
Conclusion
Both absolute and incremental encoders are good choices for assembly lines that require counts and positional information. However, they should be used in separate situations.
You should use an absolute encoder when:
- Safety is paramount and absolute position ensures safety
- You cannot afford to lose production time after a power outage
- You need an encoder that will inform you on absolute position, not just relative position or distance
You should use an incremental encoder when:
- Your project only requires counts
- You can afford to lose a bit of time to reset your encoder in case of a power outage
- If you need an encoder that can tell relative position and distance but doesn’t require absolute position information
If you still have questions about which encoder will help your project and want to know more about the difference between absolute and incremental encoders for your project, don’t hesitate to call Assumotor for help today.
Assun Motor design, manufacture and distribute high-performance DC driving systems to offer total solutions for precise driving and motion control applications.
These products include:
1. Brushless Coreless motors
2. Brushed Coreless motors
3. Planetary Gearbox
4. Encoders
5. Servo Motors
6. Servo controller and Speed drivers
7. Brakes
Latest Posts
Servo Motor Controller: How It Works, Applications & Benefits
In the realm of industrial automation and precision engineering, the ability to control motor movements with high accuracy is crucial. A servo motor...
What is a DC Motor and Its Working Principle?
A Direct Current motor, a DC motor, is an electrical instrument that is operated by direct current and transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy....
What is a DC Motor and Its Working Principle?
Understanding DC Brushless Motor Efficiency & How to Test For It
Brushless DC motors are some of the most efficient and long-lasting motors available on the market today. But what exactly makes them so efficient compared...
